Debottlenecking Gas Processing Units: Doubling Capacity with 3S Technology
In the evolving landscape of natural gas processing, operators are increasingly challenged to expand throughput without major capital investments in new infrastructure. 3S Technology Debottlenecking — the strategic enhancement of existing facilities — offers a practical and cost-effective solution.
The 3S Technology (Supersonic Separation System) represents a breakthrough in 3S Technology Debottlenecking for low-temperature separation (LTS) units and other gas processing facilities. By integrating a 3S separation module into an existing LTS train, operators can double gas processing capacity while maintaining stable product quality and minimizing energy consumption.
Principal Technological Scheme
Benefits of 3S Technology Debottlenecking
Understanding 3S Technology Debottlenecking
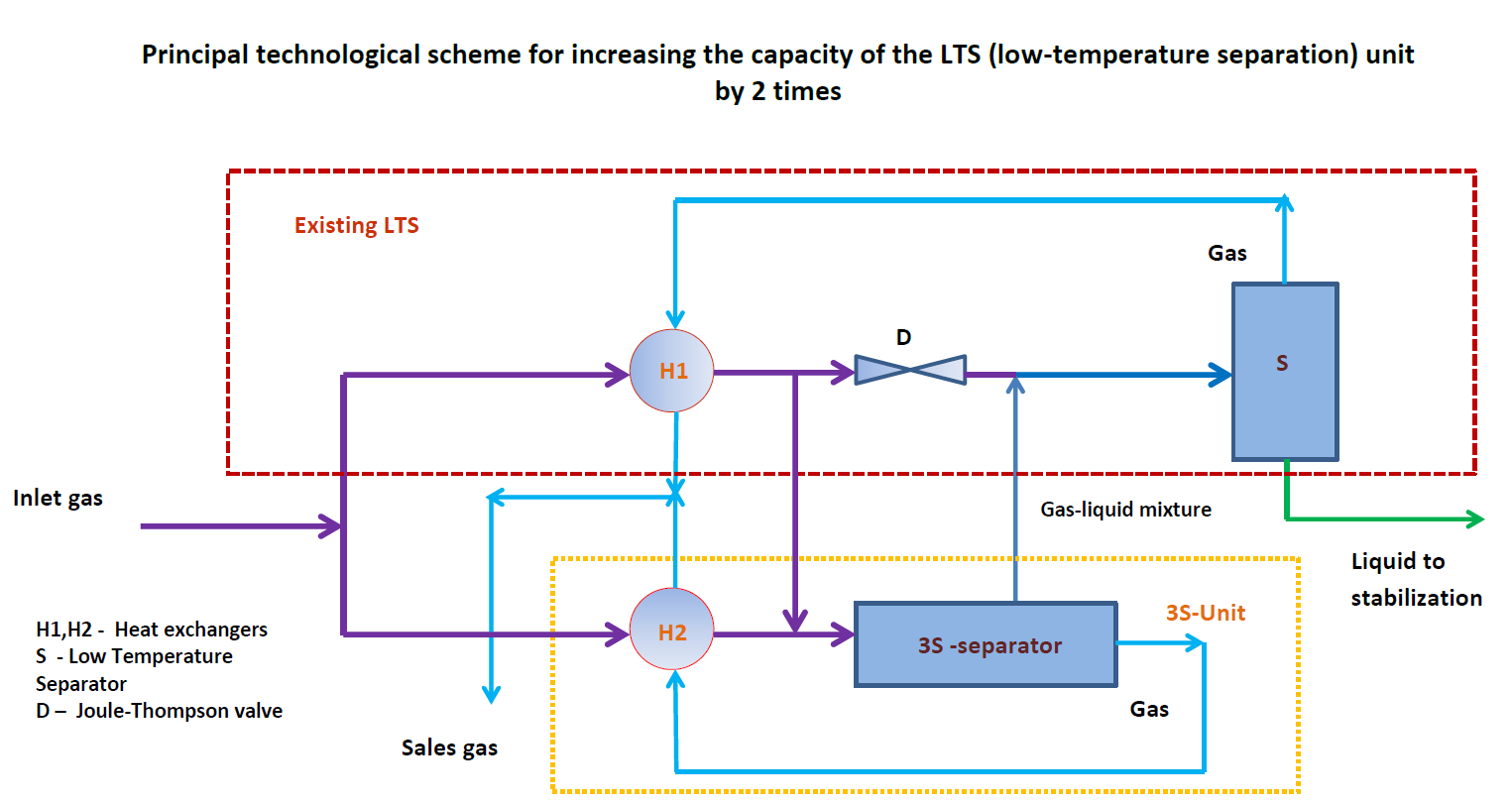
The inlet gas flow with a flow rate of 2Q is divided into two equal streams, which are cooled in H1 and H2 respectively; Valve D is closed.
The cooled flow of 2Q and pressure Pin enters the 3S-separator, where it is divided again into 2 equal flows: purified gas and gas-liquid mixture, each of which has a flow rate Q and a pressure Pout.
Some design arrangements of the 3S-separator allows achieving such separation. The purified gas enters the H2 as a cooling agent. The gas-liquid stream is directed to a low-temperature separator S, where it is separated into a gas entering H1, and an unstable liquid.
The unit should also include: an inlet separator, a dehydration unit, and an outlet CS (if necessary).
How It Works
In a conventional LTS unit, gas enters a heat exchanger and is expanded across a Joule–Thomson valve to achieve partial condensation. The resulting gas–liquid mixture is separated in a low-temperature separator. However, capacity expansion is limited by the cooling duty and pressure drop constraints.
With the 3S debottlenecking configuration, the inlet gas flow is divided into two parallel streams, each cooled separately through existing and added heat exchangers (H2 if applicable). The cooled mixture then passes through the 3S separator, where supersonic flow induces high-efficiency phase separation of the gas–liquid stream.
In the Supersonic Gas Separation process, the gas is accelerated through a Laval nozzle, resulting in an adiabatic expansion and cooling that causes heavy hydrocarbons and water to condense. The centrifugal field generated inside the separator efficiently removes the condensed droplets before the gas is recompressed or directed downstream.
The process splits the flow into:
- Purified gas, directed as a cooling medium through H2;
- Gas–liquid mixture, sent to the existing LTS separator (S) for final separation.
This arrangement effectively doubles the processing throughput (from Q to 2Q) without major redesign or replacement of core process units.
Advantages of 3S Debottlenecking
- 2× Capacity Increase — Leverages existing LTS infrastructure with minimal footprint expansion.
- Improved Efficiency — High-speed supersonic separation enhances phase disengagement and cooling performance.
- Low Energy Demand — No moving parts or external refrigeration required.
- Modular Integration — Compact 3S modules can be retrofitted into existing plant layouts.
- Enhanced Reliability — Reduces hydrate formation risks and stabilizes downstream operations.
Applications Across the Gas Value Chain
3S debottlenecking solutions can be applied across Upstream, Midstream, and Downstream sectors:
- Upstream: Expanding field-level gas treatment or flared gas recovery systems.
- Midstream: Increasing plant throughput and preventing hydrate formation during gas conditioning.
- Downstream: Ensuring steady, high-quality gas supply for petrochemical feedstock and refinery integration.
Additional Research and Knowledge Sources
- Wikipedia: Supersonic Gas Separation — Overview of the principle and applications.
- ResearchGate: Supersonic Gas Separation Technology – A Review — In-depth study of supersonic gas separation fundamentals and industrial implementation.
- ScienceDirect Topic: Supersonic Separation — Academic references and applications in gas dehydration and hydrocarbon recovery.
- OnePetro Library: Supersonic Gas Separation Papers — Peer-reviewed SPE papers on gas treatment and NGL recovery performance.
Conclusion
As the global energy market transitions toward efficiency and sustainability, 3S Technology provides a smart path forward for operators seeking to maximize the potential of existing gas processing assets. By combining compact design, low operational costs, and proven separation performance, 3S-based debottlenecking unlocks significant process capacity — without the cost and complexity of building anew.
Learn more about 3S modular solutions for gas processing, conditioning, and NGL recovery at 3S-MOST.eu.