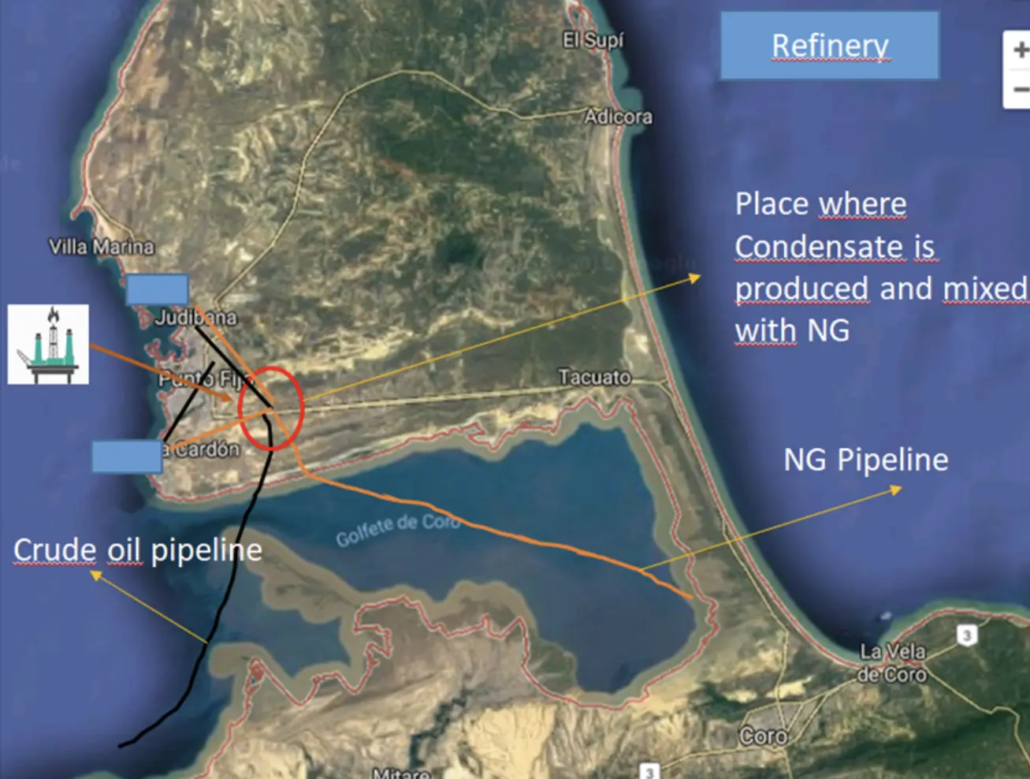
Venezuela’s Paraguaná Refining Complex (CRP), which includes the Amuay and Cardón refineries, remains a cornerstone of the country’s energy system. These facilities have opportunity and capacity to process offshore crude while receiving significant volumes of associated gas and natural gas through dedicated pipelines. However, the current gas-handling configuration leaves valuable C3–C4 fractions unrecovered.
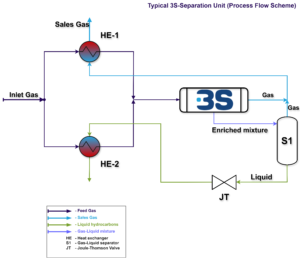
The implementation of a modern, compact and highly efficient solution — the 3S Supersonic Separation Unit — would offer PDVSA (Petróleos de Venezuela) a unique opportunity to recover these liquids and significantly improve refinery economics.
1. Current Gas Handling at CRP: Lost C3+ Value
After onshore processing, associated gas undergoes only basic condensate separation before being blended with mainland natural gas and routed to Amuay and Cardón. No fractionation or NGL recovery is performed, resulting in large volumes of propane, butane and heavier hydrocarbons remaining in the gas, unused and unmonetized.
| Refinery | Gas Flow (MMSCFD) | Gas Flow (m³/h) | Annual Volume (million m³) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amuay | 49 | 55,125 | 481 |
| Cardón | 58 | 65,250 | 573 |
This means Venezuela is currently losing thousands of tons per year of valuable C3–C4 products due to the absence of an efficient separation technology at refinery inlet points.
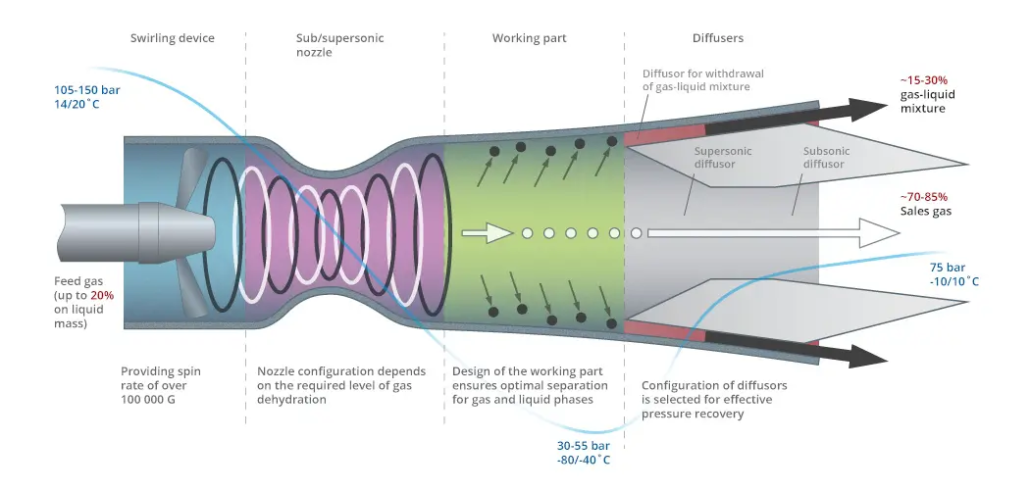
2. 3S Supersonic Separation: A Modern and Reliable Solution
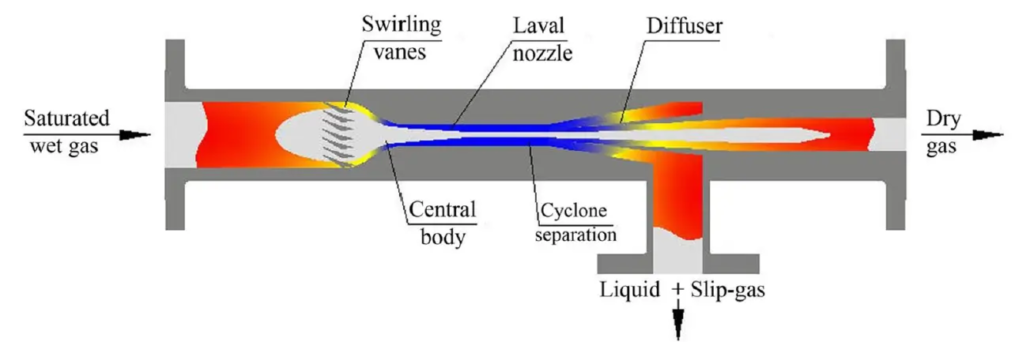
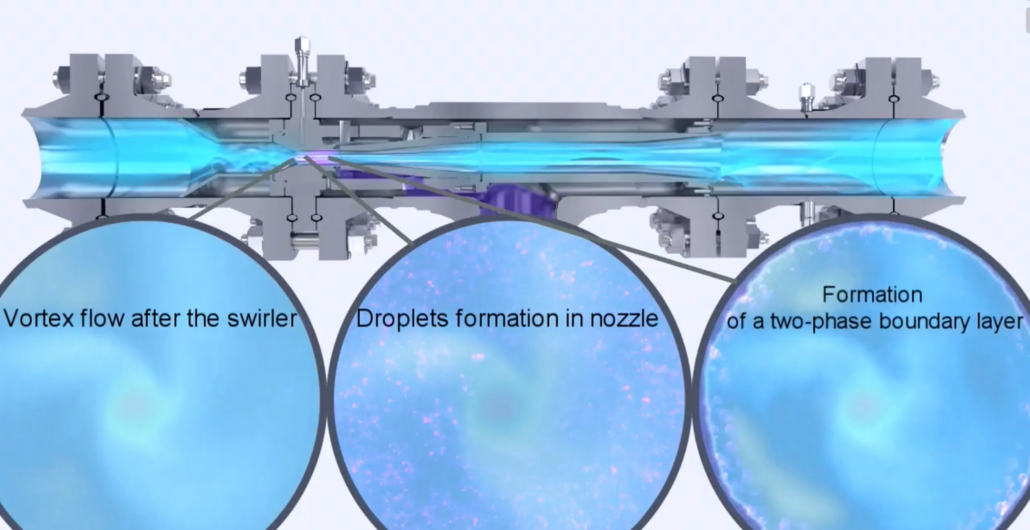
As documented in various technical materials by 3S-MOST, the 3S Supersonic Separator operates by:
- Accelerating gas through a Laval nozzle into supersonic velocity
- Inducing instant cooling and condensation of C3–C4 and water
- Separating liquids through a cyclonic mechanism without moving parts
- Operating as a compact, static, low-maintenance system
This makes it ideal for refineries like Amuay and Cardón, where reliability, footprint, and CAPEX discipline are critical factors.
Key Technical Advantages
- High C3–C4 recovery even with variable inlet compositions
- No rotating equipment — minimal maintenance
- No chemical additives or regeneration systems
- Compact skid-mounted configuration
- Suitable for unattended or remote operation
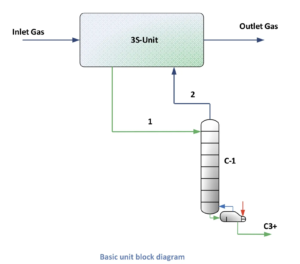
3. Recovery Potential for Amuay and Cardón
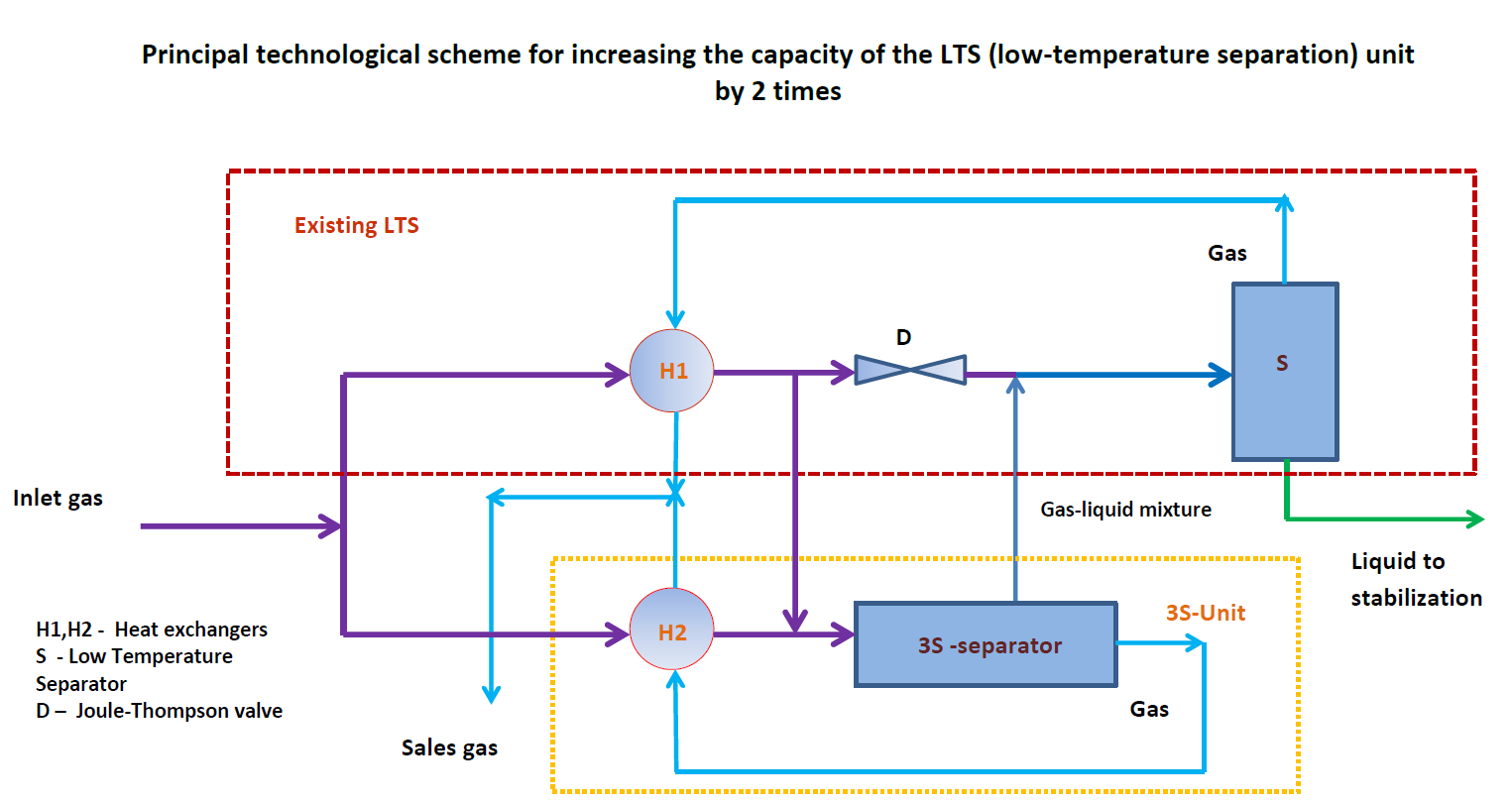
Based on the engineering evaluation, installation of 3S units (3S SuperSonic Swirl Separator) at both refineries would unlock significant NGL recovery:
| Location | Inlet Flow (MMSCFD) | Treated Flow (MMSCFD) | C3–C4 Recovery (kg/h) | C3–C4 Annual Recovery (tons/year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amuay | 49 | 48.1 | 2,418 | 21,180 |
| Cardón | 58 | 56.9 | 2,862 | 25,071 |
Total C3–C4 recovery => approximately 46,000 tons per year …
… offering a strong return even under conservative pricing assumptions.
4. Cost Estimate
Given the recovery volumes, such systems featuring 3S Supersonic Separator would typically pay for themselves rapidly.
5. Strategic Impact for Venezuela (Amuay & Cardón)
Economic Benefits
- Monetization of large C3–C4 volumes
- Increased LPG availability
- Improved refinery efficiency and stability
Operational Benefits
- Cleaner and more predictable fuel gas for refinery operations
- Reduced risk of liquids carryover
- Lower stress on compressors and furnaces
National Benefits
- Reduced flaring and emissions
- Strengthening of domestic fuel supply chains
- Modernization of a key national asset
Conclusion
The integration of 3S Supersonic Gas Separation at the Amuay and Cardón refineries offers a compelling opportunity for Petróleos de Venezuela (PDVSA) and for Venezuela’s energy sector. With high recovery efficiency, low maintenance requirements and a flexible financing structure, this technology represents an immediately actionable step toward restoring and enhancing national refining capability.
- Total C3–C4 recovery => approximately 46,000 tons per year …
In a context where every recovered barrel and every recovered molecule counts, 3S technology stands out as a practical, efficient and high-impact investment for the Paraguaná Refining Complex.
Ready to Transform Your Gas Stream into Value?
Share your latest gas analysis (composition, pressure, flow ± variability) and your processing goals. We’ll return a 3S Technology tailored block flow diagram, footprint, and payback snapshot for your site.